5 Surprising Facts About CXX in Roman Numerals
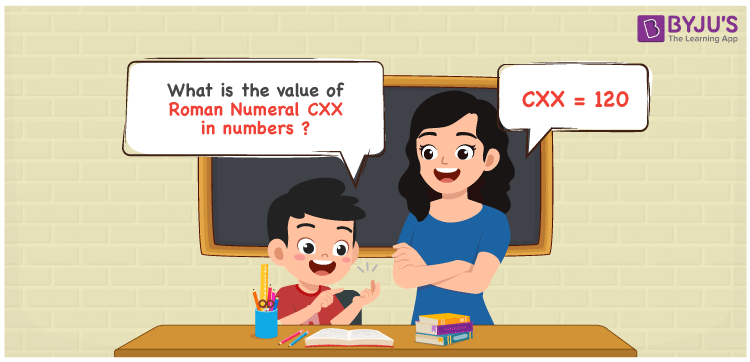
Have you ever looked at the intricate world of Roman numerals and wondered about some of their lesser-known secrets? There's a wealth of history and structure hidden within these ancient symbols, and today, we'll unveil five surprising facts about the Roman numeral CXX, which translates to 120 in our modern number system.
1. CXX Is Not As Simple As It Seems


At first glance, CXX might seem like a straightforward combination of symbols: C (100) + X (10) + X (10), equalling 120. But delve a bit deeper, and you’ll find that:
- Subtractive Notation: Roman numerals can employ subtractive notation, where smaller symbols before larger ones are subtracted from the total. For instance, IV is 4 (5-1), while IX is 9 (10-1).
- Placement Rules: There’s a rule against placing more than one smaller symbol before a larger one, but also a lesser-known rule that limits how many of the same numerals can be repeated in a sequence. Generally, three repeated symbols are allowed (e.g., XXX for 30), but exceptions exist for 4 and 9 multiples (like CM for 900).
💡 Note: Roman numerals might sometimes bend their own rules in art, architecture, or inscriptions for visual balance or stylistic reasons.
2. The Number 120 and Roman Cultural Significance

Number 120 holds special significance in Roman culture beyond just being represented by CXX:
- The Senate in ancient Rome often had around 120 senators, symbolizing stability and the collective power of the state.
- The number 120 might relate to measurements and timekeeping, as the day was divided into 24 hours, each hour into 60 minutes, and thus, six 20-minute periods made 120 minutes.
- Calendars: The Roman calendar had a peculiar structure where the months did not always align perfectly with the solar year, causing adjustments that could span over 120 days, especially during leap years.
3. CXX as a Symbol of Timekeeping and Age

Before our modern decimal system became prevalent, Roman numerals were critical in timekeeping, particularly for clocks:
- Clocks with Roman numerals, like Big Ben, would showcase CXX as noon or midnight.
- Calculating age or duration with Roman numerals was common, where someone might claim to be “CXX” years old, indicating their venerable age.
- Timekeeping Precision: Some Roman sundials were incredibly precise, able to indicate time to within minutes, showcasing the importance of accurate timekeeping.
4. The Mystical Qualities of CXX

In numerology, numbers often carry esoteric meanings:
- Gematria: In the practice of gematria, where numbers are assigned to letters, CXX could be interpreted in various ways depending on the language system used (Latin, Hebrew, or Greek).
- Cultural Symbolism: Many cultures view numbers like 120 as having mystical or symbolic significance due to its relation to age limits, life cycles, or divine perfection.
🔮 Note: While not strictly Roman, medieval European alchemy sometimes incorporated Roman numerals into their numerological and symbolic studies.
5. Modern Uses and Misuses

Despite their ancient origins, Roman numerals have found their way into modern life:
- Super Bowl Tradition: Each Super Bowl event is numbered using Roman numerals, where Super Bowl 120 would be Super Bowl CXX.
- Publishing: Roman numerals are often used in book front matter for copyright dates, but mistakenly, some might use non-standard forms like “120” instead of “CXX.”
📚 Note: Interestingly, “MCMXCVIII” (1998) instead of “1998” is preferred in some publications due to its perceived elegance or historical gravitas.
Thus, we've uncovered some intriguing facets of the Roman numeral CXX, from its structural intricacies to cultural significance, mysticism, and modern applications. This ancient numerical system remains a testament to the Romans' legacy in our understanding of numbers, time, and symbolism. Whether you're viewing a grand building, analyzing ancient texts, or simply noting the Super Bowl number, the legacy of Roman numerals, and in particular CXX, continue to fascinate and influence us in ways we might not always recognize.
Can you write numbers larger than 3999 in Roman numerals?

+
Yes, though less common, larger numbers can be written by using a horizontal bar above a Roman numeral to multiply its value by 1,000.
What’s the difference between Roman and Arabic numerals?

+
Roman numerals use letter symbols to represent numbers, while Arabic numerals, also known as Hindu-Arabic, use digits (0-9) and positional notation.
Why are Roman numerals still used today?

+
Their use in today’s world adds a touch of tradition and formality to things like book publishing, clock faces, movie release years, and ceremonial events.



